|
|
IOTC Platform Ver: [Comments] |
- Basic Concept
Copyright (c) 2010 by Throughtek Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
This document describes the basic concepts of TUTK IOTC platform. It is organized in five parts: the first part is explanation of those terminologies used in IOTC platform, the second part mentions the four key participates in IOTC platform and their responsibility, the third part details about the collaboration among these participates to provide an overview of IOTC platform, the fourth part briefly describes the three important data communication modules in IOTC platform and their relationship and the final part discusses the penetration capability of IOTC platform.
Terminology
· IOTC Platform – Internet of Things Cloud platform, a solution provided by TUTK to enable P2P connections among devices and clients with simple configurations to transfer variant types of data
· Master – A machine, maintained by TUTK, in IOTC platform to manage servers and devices as well as authenticate them by checking internal key information
· Server – A machine, maintained by TUTK or device manufactures, in IOTC platform to handle connection among devices and clients with P2P or relay service
· Device – An equipment made by a vendor to be capable of IOTC platform and can be connected by clients even if the device is put behind NAT
· Client – A terminal connecting to devices to have in-between data communicated
· UID – A twenty-byte unique identification issued by TUTK for each server and device for management and connection purpose
· VPG – A set of ID to denote vendor, product and group ID, respectively, and it is part of factors to generate UID
· IOTC Module – A kind of data communication modules to provide basic data transfer among devices and clients
· IOTC Session – A connection established between a device and a client, while a device can have multiple sessions with multiple clients and vice versa
· IOTC Channel – A communication path in a session for read and write data between a device and a client, while a session can have multiple channels to transfer data simultaneously
· RDT Module – A kind of data communication modules in IOTC platform to provide Reliable Data Transfer among RDT servers and RDT clients in bi-directional way
· RDT Server – The device that uses RDT for transferring or receiving data with RDT client
· RDT Client – The client that uses RDT for transferring or receiving data with RDT server
· RDT Channel – The channel, based on an IOTC channel, established between a RDT server and a RDT client, and a RDT server can have multiple RDT channels with a RDT client
· AV Module – A kind of data communication modules in IOTC platform to provide fluent streaming Audio / Video data from AV servers to AV clients in unidirectional way
· AV Server – The device or client which transfer audio or video to corresponding AV client
· AV Client – The device or client which receives audio or video from corresponding AV server
· AV Channel – The channel, based on an IOTC channel, established between a AV server and a AV client, and a AV server can have multiple AV channels with a AV client
· AV IO Control – A set of commands, such as play, stop… etc., used in AV communication module defined by device manufactures for communication between a AV server and a AV client
· Tunnel server – A device with P2PTunnel module to be connected by Tunnel agents even if the device is behind NAT.
· Tunnel agent – A client with P2PTunnel module to connect to Tunnel server for P2P communication.
· AES – A kind of industrial encryption ways supported by IOTC platform to secure the data transferred among devices and clients.
Role and Responsibility
In IOTC platform, master, server, device and client are four key participates collaborating each other to achieve P2P or relay communication service with easy configuration on device and client. Followings are their major responsibilities charged in IOTC platform.
· Master
o Authenticate UID of servers and devices
o Manage connected servers
o Provide devices and clients about the lists of servers matched to specific VPG
· Server
o Manage login devices
o Provide clients P2P or relay service to communicate with devices
· Device
o Login into servers matched to specific VPG
o Listen for connection from client
o Communicate with clients
· Client
o Ask masters to provide a list of servers matched to specific VPG of a device
o Ask servers to help establish connection with devices
o Communicate with devices
· Tunnel server
o Login Servers by UID
o Listen for connection request from Tunnel agent
o Communicate with Tunnel agent
· Tunnel agent
o Request Masters to provide a list of Servers via UID
o Request Servers to establish P2P connection with Tunnel server
o Communicate with Tunnel server
Collaboration
The diagram below depicts the collaboration relationship among master, server, device and client in IOTC platform.
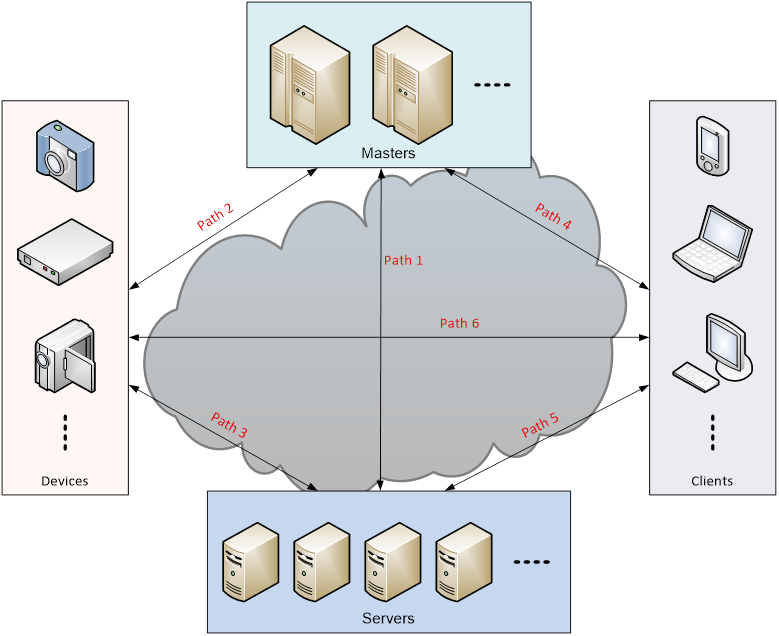
Fig.1 The collaboration of master, server, device and client in IOTC platform
Six paths are defined in the diagram above and their co-working behaviors between peers are described below. Please note that the following co-working behaviors are typical and generic. For the sake of easy explanation, error handling or detail back and forth communication are tentatively omitted.
· Path 1
o When a server starts up, it will connect to selected masters by providing its UID.
o Masters will check if the UID of the server is certificated or not. If servers can be recognized by masters, the server information, for example, IP address and VPG, will be stored inside masters.
· Path 2
o When a device wants to join IOTC platform, it will first connect to selected masters with device’s UID.
o Masters will check if the UID of the device is certificated or not. If ok, masters will feedback to the device a list of connectable servers that have matched VPG to device’s one.
· Path 3
o Once a device gets the list of connectable servers from masters, it will login to those servers with device’s UID.
o The servers will check if the UID of the device is valid or not. If ok, servers will store device’s information inside and reply to the device that login process is done.
o The device will start to listen for any connection from clients once login is performed successfully with servers.
· Path 4
o When a client wants to leverage services of IOTC platform, it will connect to selected masters and inquiry a list of servers that manage the device with specified UID.
o Masters will feedback the list of servers to the client.
· Path 5
o Once a client gets the list of servers from masters, it will ask those servers to establish a connection with specified device.
o The servers will create P2P or relay communication services between the device and the client based on network status.
· Path 6
o The connection between a device and a client is ready, data can be transferred in-between.
o Three kinds of data communication modules can be used here for different purposes: IOTC module, Reliable Data Transfer (RDT) module and Audio / Video data transfer (AV) module.
Data Communication Modules
In IOTC platform, three kinds of data communication modules are provided.
· Type 1 - IOTC basic data transfer (IOTC) module
· Type 2 - Reliable data transfer (RDT) module
· Type 3 - Audio / Video data transfer (AV) module
By design, RDT module and AV module leverage the services from IOTC module while providing more specific data transfer way. Their relationship can be depicted as following diagram.
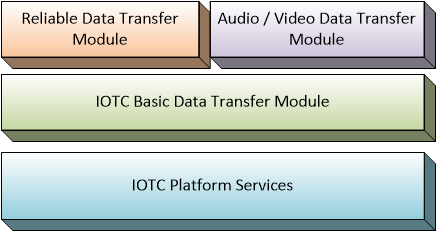
Fig.2 The relationship of three kinds of data transfer modules in IOTC platform
In RDT module, the data is transferred in reliable way to ensure all data will be received correctly. In the other hand, AV module lets the multimedia data be transferred in managed way, i.e. audio data is tried to be synchronized with frame data and kept smooth according to network status.
Since the purpose of these three kings of data communication modules are different, their benefit and overhead are also different from each other. Therefore, it is suggested to investigate what kinds of application features to be developed in devices and clients, then select appropriate one from these three kinds of data communication modules.
IOTC P2P Tunnel Module
A Tunnel connection is to provide a private path of transmission through a public network. As follows, it depicts the supported protocols by IOTC P2PTunnel module, and Fig.3 expresses the schematic diagram.
|
Service |
Protocol |
Served Port |
|
HTTP |
TCP |
80 |
|
SSH |
TCP |
22 |
|
TELNET |
TCP |
23 |
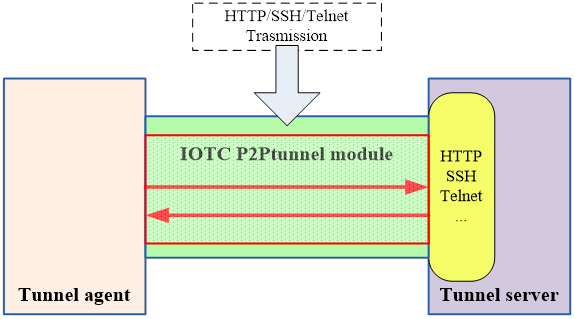
Fig.3 IOTC P2PTunnel module schematic diagram
Penetration Capability
There are four types of network address translation (NAT) mechanism that are commonly used in current network environment (please refer NAT wiki for more detail).
By using IOTC platform, devices and clients can leverage P2P communication with following NAT combination.
|
Case |
NAT Type in A Device |
NAT Type in A Client |
|
1 |
Full-cone NAT |
Full-cone NAT |
|
2 |
Full-cone NAT |
(Address) restricted cone NAT |
|
3 |
Full-cone NAT |
Port-restricted cone NAT |
|
4 |
Full-cone NAT |
Symmetric NAT |
|
5 |
(Address) restricted cone NAT |
Full-cone NAT |
|
6 |
(Address) restricted cone NAT |
(Address) restricted cone NAT |
|
7 |
(Address) restricted cone NAT |
Port-restricted cone NAT |
|
8 |
(Address) restricted cone NAT |
Symmetric NAT |
|
9 |
Port-restricted cone NAT |
Full-cone NAT |
|
10 |
Port-restricted cone NAT |
(Address) restricted cone NAT |
|
11 |
Port-restricted cone NAT |
Port-restricted cone NAT |
|
12 |
Symmetric NAT |
Full-cone NAT |
|
13 |
Symmetric NAT |
(Address) restricted cone NAT |
However, relay mode will be used for communication between devices and clients if matching to following NAT combination, which means P2P connection cannot be established between Tunnel server and Tunnel agent.
|
Case |
NAT Type in A Device |
NAT Type in A Client |
|
1 |
Port-restricted cone NAT |
Symmetric NAT |
|
2 |
Symmetric NAT |
Port-restricted cone NAT |
|
3 |
Symmetric NAT |
Symmetric NAT |
IOTC relay service always works as long as both Tunnel server and Tunnel agent can connect to the Server. Since there is no more efficient technique that works reliably on all existing NAT techniques, relay service is a very useful strategy if the robustness of connection is considered.